What to study for your java backend job interview
Posted on July 18, 2023 • 33 minutes • 7018 words • Other languages: Español
A guide to possible questions you may encounter in your next interview.
Introduction
This is quite a long article. It consists of 25 questions that I used as practice for my last interview.
Obviously, this is not a guarantee that with this knowledge you will land your dream job. But at least for me, an Argentine programmer without a university degree with a year and a half of work experience, it helped me find a job in dollars.
(AFIP if you’re reading this, my Ecuadorian salary goes to a British account, so you have no power here, gg)
Java in general
1. In Java, what is the difference between an interface and an abstract class?
In Java, an interface is a collection of abstract methods that define a set of behaviors or capabilities that a class can implement. An abstract class, on the other hand, is a class that cannot be instantiated and can contain abstract and non-abstract methods.
Here are some of the key differences between interfaces and abstract classes:
| Abstract Class | Interface |
|---|---|
| It has both concrete methods and abstract methods | You can only have abstract methods |
| You can only extend a single abstract class | You can implement any number of interfaces |
| You can have a constructor method | You cannot have a constructor method |
| Attributes can have any visibility | Attributes can only be public |
| You can have instance variables | Cannot have instance variable |
In short, interfaces are used to define a set of behaviors that a class must implement, while abstract classes provide a common implementation and behavior that their subclasses can inherit.
2. In your own words, could you describe what an interface is?
An interface in Java is a model for a set of related methods that define a contract or a set of behaviors that a class must implement. It provides a way for different objects to communicate with each other without knowing their specific implementation details.
An interface is defined by the interface keyword and contains only method signatures (ie method name, parameters, and return type), but no implementation details. A class that implements an interface must provide an implementation for all methods defined on the interface.
Interfaces are useful in situations where we need to define a common set of behaviors that different classes can implement in their own way. For example, the Comparable interface in Java defines a compareTo() method that can be implemented by any class that wants to be comparable to other objects. This allows us to sort objects of different classes using the same algorithm.
In general, interfaces provide a powerful mechanism for abstraction and decoupling in Java programs, and they play a key role in defining APIs and designing software systems that are flexible, extensible, and maintainable.
3. When is a static method useful?
A static method is a method that belongs to a class rather than an instance of that class. Static methods can be called on the class itself without creating an instance of the class. Here are some situations where static methods can be useful:
-
Utility methods – Static methods can be used to define utility methods that perform common operations that do not require an instance of the class. For example, the
Mathclass in Java has several static methods such asMath.max()andMath.min()that are frequently used in mathematical calculations. -
Factory Methods – Static methods can be used to define factory methods that create instances of the class. For example, the
getInstance()method in theSingletondesign pattern is a static method that returns the single instance of the class. -
Helper Methods: Static methods can be used to define helper methods that use other methods of the class. For example, a static method could be used to validate the input parameters of a non-static method in the same class.
-
Performance optimization: Static methods can improve performance by reducing object creation and garbage collection overhead. Since static methods do not require an instance of the class to be created, they can be more efficient when called frequently.
-
Simplicity and readability: Static methods can make code simpler and more readable by avoiding the need to create an instance of the class. This can be particularly useful for simple stateless operations.
However, it is important to use static methods wisely and only when appropriate. Excessive use of static methods can make code more difficult to test and maintain, and can lead to code that is tightly coupled and difficult to change.
Java 8
4. What substantial improvements were introduced in Java 8?
Java 8 introduced several significant enhancements to the Java language and platform. These are some of the most important:
-
Lambdas: Java 8 introduced support for lambda expressions, which are a new way of writing concise, functional code. Lambdas make it easy to write code that is more expressive and easier to read, especially for operations like filtering, mapping, and collection shrinking.
-
Stream API: Java 8 also introduced the Stream API, which provides a powerful and flexible way to process collections of data. The Stream API works seamlessly with lambda expressions and makes it easy to write code that is concise and expressive.
-
Default methods on interfaces: Java 8 allows interfaces to have default methods, which provides a way to add new functionality to an interface without breaking existing implementations. This makes it easy to evolve interfaces over time without introducing backward compatibility issues.
-
Date and Time API: Java 8 introduced a new Date and Time API that provides a more flexible and powerful way of working with dates and times. The new API makes it easy to perform common operations like calculating the difference between two dates or formatting a date for display.
-
Optional class: Java 8 introduced the optional class, which provides a way to handle null values in a more expressive and concise way. The Optional class makes it clear when a value may be absent and forces developers to handle that case explicitly.
-
Nashorn JavaScript Engine: Java 8 also introduced the Nashorn JavaScript engine, which provides a way to execute JavaScript code within a Java application. This makes it easier to integrate JavaScript code into Java applications and provides a more consistent way to handle scripting tasks.
Overall, Java 8 introduced several important enhancements to the Java language and platform, making it easier to write expressive, functional, and maintainable code.
5. Explain some functional programming concepts: API Streams, method reference, functions as first class citizens, anonymous functions (lambda expressions)
API Streams
The Streams API is one of the major features introduced in Java 8, which provides a functional programming approach to processing collections of objects. It allows developers to perform operations like filtering, sorting, and mapping on a collection in a more concise and efficient way.
Flows are made up of three main components:
- Source: a collection of objects or an array.
- Intermediate operations: Operations that transform the flow into another flow. Examples include filter(), map(), and sorted().
- Terminal operations: Operations that produce a result or a secondary effect. Examples include forEach(), count(), and reduce().
This is an example of using the Streams API to filter a list of names beginning with the letter “A” and print them:
List<String> names = Arrays.asList("Alice", "Bob", "Amy", "John");
names
.stream()
.filter(name -> name.startsWith("A"))
.forEach(System.out::println);
This code will print:
Alice
Amy
This is just a simple example, but the Streams API can be used for much more complex operations on collections, such as grouping, joining, and aggregating data.
The Streams API has many advantages, such as better readability, modularity, and parallelization. By using the Streams API, developers can write more concise and expressive code that is easier to read and maintain.
Method Reference
Method reference is a shorthand syntax that allows you to refer to an existing method by name instead of writing a lambda expression that calls the method. For example:
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
// Using lambda expression
numbers.stream().forEach(n -> System.out.println(n));
// Using method reference
numbers.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
Functions as First Class Citizens
Functions as first-class citizens refer to the ability to treat functions as values that other functions can pass and return. In Java, this is accomplished by using functional interfaces such as java.util.function.Function and java.util.function.Predicate. For example:
Function<String, Integer> stringLength = String::length;
int length = stringLength.apply("hola"); // length will be 5
Lambda expressions
Lambda expressions are anonymous functions that can be used as values, just like regular functions. They are often used with functional interfaces to provide a more concise way of writing code. For example:
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
// Using anonymous function
numbers.stream().filter(n -> n % 2 == 0).forEach(System.out::println);
// Using lambda expression
numbers.stream().filter((Integer n) -> { return n % 2 == 0; }).forEach(System.out::println);
In general, these functional programming concepts help make Java code more concise, expressive, and modular. They can also make it easier to write code that is more maintainable and scalable.
Spring Boot
6. What is Spring Boot?

Spring Boot is an open source Java-based framework that makes it easy to build production-grade Spring-based applications that can be deployed and run without requiring a complex configuration process.
Spring Boot provides a set of preconfigured templates and feedback that allow developers to quickly build, test, and deploy their applications with minimal configuration. It simplifies configuration of Spring-based applications by providing sensible defaults and automatic configuration of commonly used libraries, reducing the need for manual configuration.
Some of the key features of Spring Boot include:
-
Embedded server support: Spring Boot includes an embedded Tomcat, Jetty, or Undertow server that can be used to run the application without the need to install a separate web server.
-
Automatic configuration: Spring Boot automatically configures the application based on the libraries that are available on the classpath, which reduces the need for manual configuration.
-
Startup dependencies: Spring Boot provides a set of startup dependencies that simplify the configuration of common libraries such as Spring Data, Spring MVC, and Spring Security.
-
Actuator: The Spring Boot Actuator provides a set of production-ready features such as health checks, metrics, and monitoring that can be easily added to your application.
Overall, Spring Boot is a powerful framework that simplifies the development of Spring-based applications by reducing the amount of boilerplate code and configuration required. It has gained widespread adoption among Java developers due to its ease of use, flexibility, and community support.
7. What are the following annotations used for? @RestController @Service @Repository Can you name others besides these?
@RestController– This annotation is used to indicate that a class is a RESTful web service controller, meaning that it handles incoming HTTP requests and produces HTTP responses in a format such as JSON or XML. Methods in a@RestControllerclass are typically annotated with HTTP method annotations such as@GetMapping,@PostMapping,@PutMapping, or@DeleteMapping.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ExampleController {
@Autowired
private ExampleService exampleService;
@GetMapping("/example")
public String getExample() {
return exampleService.getExampleData();
}
@PostMapping("/example")
public void createExample(@RequestBody String data) {
exampleService.createExampleData(data);
}
@PutMapping("/example/{id}")
public void updateExample(@PathVariable String id, @RequestBody String data) {
exampleService.updateExampleData(id, data);
}
@DeleteMapping("/example/{id}")
public void deleteExample(@PathVariable String id) {
exampleService.deleteExampleData(id);
}
}
@Service– This annotation is used to indicate that a class is a service component in a Spring application, meaning that it contains business logic that can be used by various parts of the application. A@Serviceclass typically interacts with repositories or other data access components to perform CRUD (create, read, update, delete) operations on domain objects.
@Service
public class ExampleService {
@Autowired
private ExampleRepository exampleRepository;
public Example getObjectById(Long id) {
return exampleRepository.findById(id);
}
public void createObject(Example object) {
exampleRepository.save(object);
}
public void updateObject(Example object) {
exampleRepository.save(object);
}
public void deleteObject(Long id) {
exampleRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}
@Repository– This annotation is used to indicate that a class is a repository component in a Spring application, meaning that it provides access to a data source such as a database, file system, or API external. A@Repositoryclass usually contains methods to read, write, and query data from the data source.
@Repository
public class ExampleRepository {
public void saveData(String data) {
// save logic
}
public String fetchData() {
// fetch logic
return "Example Data";
}
public void deleteData() {
// delete logic
}
}
Other commonly used annotations in Spring applications include:
-
@Autowired: This annotation is used to inject dependencies into a bean managed by Spring. It can be used in parameters, fields, or constructor methods. -
@Configuration: This annotation is used to indicate that a class is a configuration component in a Spring application, which means that it contains configuration options and bean definitions that are used to configure the application context. -
@Component: This annotation is used to indicate that a class is a generic bean managed by Spring. It is often used as a general annotation for classes that do not fit into one of the more specific annotation categories. -
@PathVariable: This annotation is used to indicate that a method parameter should be filled with a value from a URL path variable. -
@RequestBody: This annotation is used to indicate that a method parameter should be filled with the request body of an incoming HTTP request.
There are many other annotations provided by Spring and its extensions, each serving a specific purpose in building Spring applications.
8. Explain the most commonly used Java annotations for data modeling with Hibernate and data serialization with Jackson
- @Entity – Used to annotate a Java class that is an entity in a database table.
- @Id: used to specify the primary key of an entity.
- @GeneratedValue: used to specify the strategy for generating the values of the primary keys.
- @Column – Used to specify the mapping between a Java class field and a database column.
@Entity
@Table(name = "example_table")
public class ExampleEntity {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private Long id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "age")
private int age;
// Constructor, getters and setters
}
Some popular Java annotations used for data serialization with Jackson are:
- @JsonFormat – Used to specify the format of a date or time field.
- @JsonProperty – Used to specify the name of a property in the JSON output.
- @JsonIgnore – Used to ignore a property during JSON serialization and deserialization.
- @JsonInclude – Used to specify when a property should be included in the JSON output, based on its value.
public class ExampleData {
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd")
private Date dateOfBirth;
@JsonProperty("full_name")
private String fullName;
@JsonIgnore
private String password;
@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL)
private String address;
// Getters and setters
}
9. What is the @Slf4j annotation? Why is it useful?
The @Slf4j annotation is a Lombok annotation that can be used to automatically generate registration code in a Java class. The annotation is normally placed at the class level, just above the class declaration.
When the @Slf4j annotation is used, Lombok generates a private static final field called log in the class, which is initialized to a logger instance using the Simple Logging Facade for Java (SLF4J) API. The generated logger can be used to log messages at different severity levels (eg debug, info, warning, error) using the methods provided by the SLF4J API.
For example, the following code demonstrates how to use the @Slf4j annotation to generate a logger in a Java class.
@Slf4j
public class MyClass {
public void doSomething() {
log.info("Doing something...");
// ...
}
}
In this example, Lombok generates the following code for the MyClass class:
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class MyClass {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyClass.class);
public void doSomething() {
log.info("Doing something...");
// ...
}
}
The @Slf4j annotation is useful because it allows developers to easily add registration code to their classes without having to write boilerplate code. It also ensures that the logger instance is initialized correctly and provides a consistent, standard logging interface throughout the codebase. Also, using a logging framework like SLF4J can improve logging code performance by avoiding unnecessary string concatenation when creating log messages.
10. What advantages can you mention of using spring-webflux?
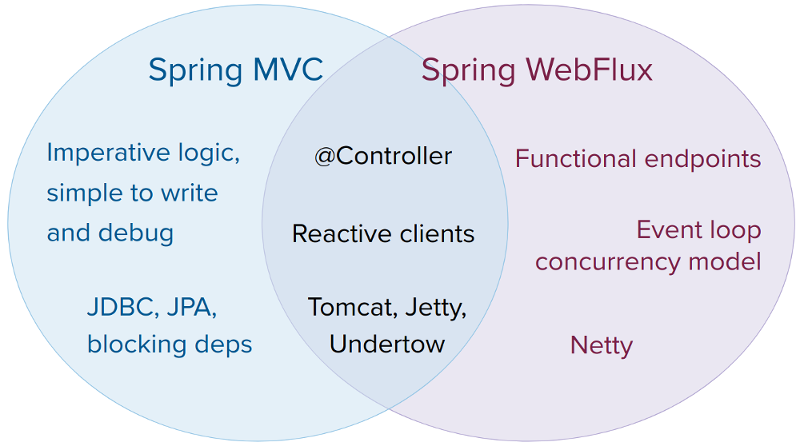
-
Reactive Programming Model: Spring WebFlux is designed with a reactive programming model that allows you to build more responsive and resilient applications. Reactive programming is a programming paradigm that allows you to build applications that can react to events and handle large numbers of concurrent requests with minimal overhead.
-
High scalability: Spring WebFlux is based on the Reactor library, which provides a powerful set of tools for building reactive applications. These tools make it possible to handle high levels of concurrency and easily scale up and down as demand changes.
-
Non-blocking I/O: Spring WebFlux uses non-blocking I/O, which means it can handle many requests without blocking threads. This makes it possible to create applications that are more responsive and can handle more traffic without increasing hardware requirements.
-
Light Footprint: Spring WebFlux has a light footprint, which means it can be deployed in resource-constrained environments. This makes it ideal for building cloud-native applications and microservices that need to be deployed on a variety of platforms.
-
Integration with other Spring modules: Spring WebFlux is part of the larger Spring ecosystem, which means that it integrates seamlessly with other Spring modules, such as Spring Boot, Spring Data, and Spring Security. This makes it easy to build end-to-end applications using Spring.
-
Support for multiple protocols: Spring WebFlux supports multiple protocols such as HTTP, WebSocket, and TCP. This makes it possible to create applications that can handle a variety of data streams and communication patterns.
Overall, Spring WebFlux is a powerful tool for building responsive, scalable, and reactive applications. It offers a number of advantages over traditional blocking I/O frameworks and is ideal for building microservices and cloud-native applications.
11. What is gradle?

Gradle is an open source build automation tool used to automate the process of building, testing, and deploying software projects. It is designed to be highly customizable and flexible, making it ideal for a wide range of projects and development workflows.
Gradle uses a Groovy-based Domain Specific Language (DSL) to define build scripts that automate the various tasks involved in the build process. These tasks may include compiling source code, running tests, generating documentation, and packaging the final application.
Gradle is known for its powerful dependency management capabilities, which make it easy to manage complex project dependencies and ensure that all necessary libraries and frameworks are available to the project.
Gradle also has a large and active community of developers, who have contributed many plugins and extensions that can be used to extend the functionality of the tool. This means it’s easy to find plugins for a wide range of tasks, such as code quality analysis, code coverage reporting, and deployment to cloud platforms.
Many companies and organizations use Gradle to automate their software development processes, including Google, Netflix, LinkedIn, and Airbnb, among others. Its popularity has grown rapidly in recent years and it is now one of the most widely used build automation tools in the Java ecosystem.
Architecture
12. What is the difference between a monolithic service and a microservice?
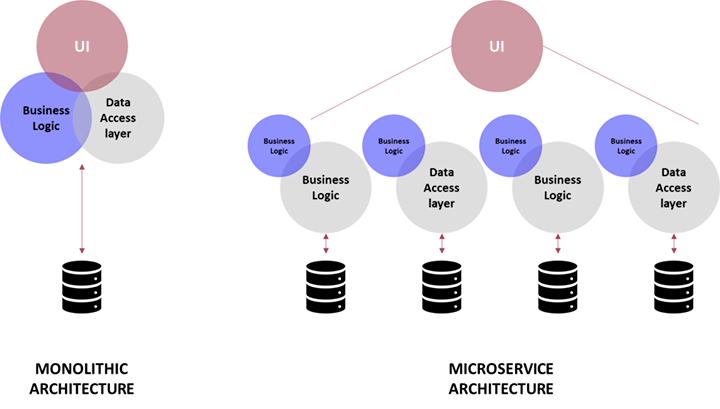
A monolithic service is a software architecture in which all the components of an application are tightly coupled and implemented together as a single unit. In a monolithic service, the application code is organized into one or more modules, but all modules share the same process and run in a single runtime environment.
On the other hand, a microservices architecture is an approach in which an application is built as a collection of small independent services that are loosely coupled and communicate with each other over a network. In a microservices architecture, each service is responsible for a specific business capability and can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently of the other services.
The main difference between a monolithic and a microservice architecture is the way the application is organized and deployed. Monoliths are typically easier to initially develop and deploy, as they require less setup and infrastructure. However, as the application grows in size and complexity, it becomes more difficult to maintain and scale, as any change to one part of the application can potentially affect the entire system.
By contrast, microservices offer greater flexibility and scalability as they are designed to be loosely coupled and independently deployed. Each microservice can be developed and maintained by a separate team, allowing for greater agility and faster time to market. However, microservices can be more complex to develop and manage, as they require more infrastructure and tools to handle the distributed nature of the architecture.
In general, the choice between a monolithic and a microservice architecture depends on the specific needs of the application and the organization developing it. Both architectures have their advantages and disadvantages, and the decision should be based on factors such as scalability, maintainability, agility, and the skills and resources available to the development team.
13. What is the purpose of BDD?
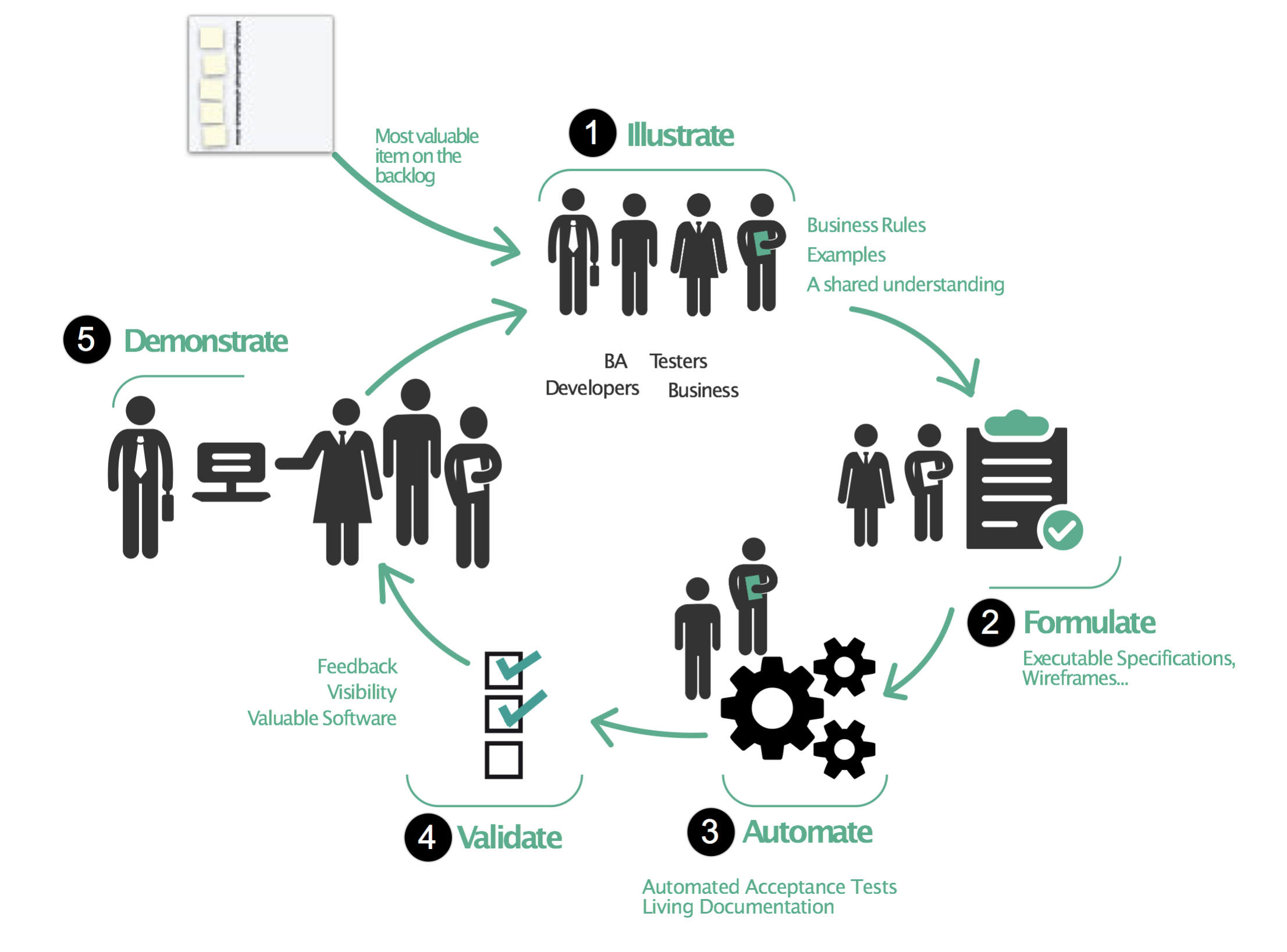
The purpose of Behavior Driven Development (BDD) is to provide a framework and methodology for developing software that focuses on delivering business value by aligning the development process with desired system behavior.
BDD aims to improve collaboration between developers, testers, and commercial stakeholders by providing a common language and framework to describe and understand system behavior. BDD encourages stakeholders to define the desired behavior of the system using natural language, which can be understood by all parties involved in the development process.
BDD also emphasizes the importance of automating the testing process, using tools like Cucumber or JBehave to translate natural language descriptions of the desired behavior into executable tests. This helps ensure that the code being developed is aligned with the desired behavior of the system and that changes to the code do not inadvertently introduce regressions or break existing functionality.
By focusing on system behavior and involving all stakeholders in the development process, BDD can help ensure that the software being developed delivers the desired business value and meets the needs of users. It also promotes collaboration, communication, and a shared understanding of the project goals.
Databases
14. What type of database is redis?

Redis is an in-memory key-value database that can be used as a cache, message broker, or data store. It is designed to be fast, scalable, and reliable, and is often used to support real-time applications such as chat applications, gaming applications, and financial trading platforms.
Redis is a NoSQL database, which means it doesn’t use a traditional relational database model. Instead, it uses a simple key-value model, where each value in the database is associated with a unique key. Redis supports a wide range of data structures, including strings, hashes, lists, arrays, and ordered sets, making it a flexible and versatile database that can be used for a wide range of applications.
One of the key features of Redis is its in-memory data storage, which allows it to deliver fast read and write performance. Redis also includes built-in support for replication and clustering, allowing it to scale out to handle large amounts of data and traffic.
Overall, Redis is a powerful and flexible database that can be used for a wide range of applications, and its speed and scalability make it a popular choice for high-traffic and real-time applications.
15. According to RDBMS (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MSSQL, Oracle) theory, what is a View and how is it used?
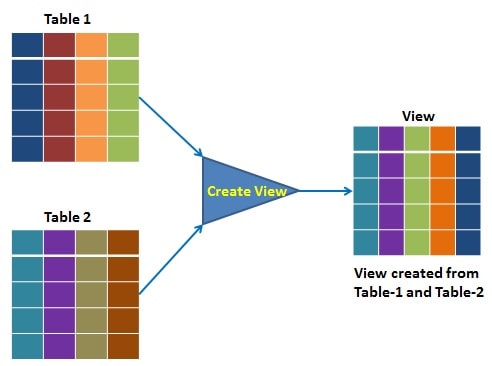
In relational database management systems (RDBMS) such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, MSSQL, and Oracle, a view is a virtual table that is derived from one or more existing tables or views in the database. A view does not contain any data of its own, but is instead a saved SELECT statement that is executed each time the view is queried.
Views are used to simplify complex queries, provide an extra level of security, and improve performance by allowing frequently used queries to be saved and reused. Here are some common use cases for views:
-
Simplify complex queries: If a query requires multiple joins, complex calculations, or other complicated operations, it can be difficult to write and maintain. A view can be created to simplify the query and make it easier to understand and work with.
-
Improve performance – If a query is executed frequently, it may be beneficial to create a view to cache the results. This can improve performance by reducing the amount of time required to execute the query each time it is executed.
-
Provide an additional layer of security: Views can be used to restrict access to sensitive data by exposing only a subset of the underlying tables. For example, a view could be created to allow users to view customer information without exposing sensitive financial data.
-
Provide a consistent interface – If multiple applications or users need to access the same data, a view can provide a consistent interface that abstracts away the underlying complexity of the database schema.
To create a view in a relational database, you would use the CREATE VIEW statement followed by a SELECT statement that defines the view. Once a view has been created, it can be queried like any other table in the database. Any changes made to the underlying tables or views will be reflected in the view when it is queried.
-- Create view
CREATE VIEW example_view AS
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table1
WHERE condition;
-- Query the view
SELECT * FROM example_view;
16. What is the main difference between an RDBMS and NoSQL databases (Redis, MongoDB)?
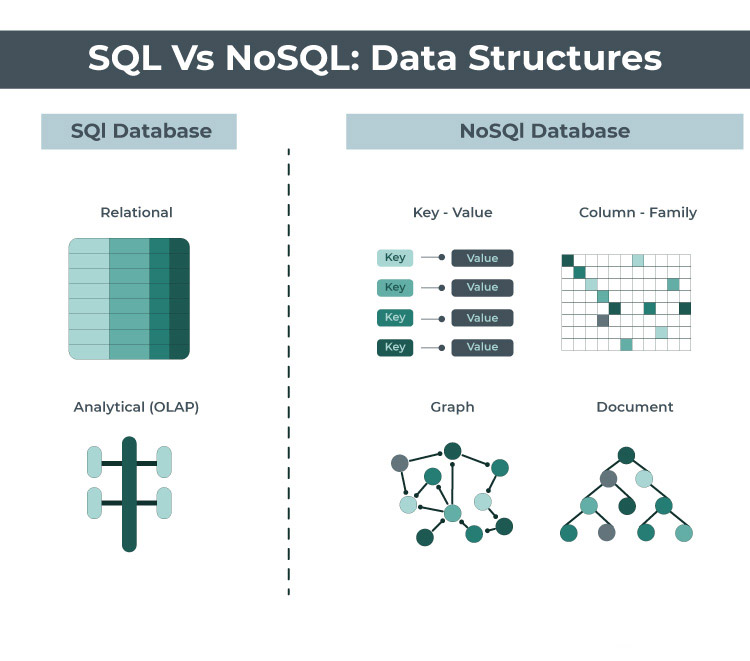
The main difference between a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) and a NoSQL database like Redis or MongoDB is the way the data is stored and accessed.
RDBMS is based on the relational model, where the data is organized in tables, and each table consists of a set of rows and columns. RDBMS uses SQL (Structured Query Language) to manipulate and query data. RDBMS is ideal for storing structured data that requires complex relationships between entities. Examples of RDBMS include MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server.
NoSQL databases, on the other hand, are not based on a fixed schema and allow for more flexible data models. NoSQL databases are designed to handle large amounts of unstructured and semi-structured data, making them ideal for big data applications. NoSQL databases do not use SQL to query data and instead use APIs or proprietary query languages. Examples of NoSQL databases include MongoDB, Redis, Cassandra, and Amazon DynamoDB.
| Feature | SQL | NoSQL |
|---|---|---|
| Main focus | Data integrity | Quickly scale and adapt in the face of change |
| Data model | Tables following a fixed scheme | Flexible schema: JSON, key-value pairs, tables with dynamic schema, graphs with vertices and edges |
| Query language | SQL | Own query languages / apis |
| Scalability | Vertical: scale with a bigger server | Horizontal: scale across multiple servers |
17. What is H2?
H2 is an open source in-memory database written in Java. It is a relational database management system that provides a small, fast, and lightweight alternative to traditional database systems like MySQL, Oracle, or PostgreSQL. H2 supports SQL and JDBC APIs, and can be used as a stand-alone database or embedded in Java applications.
One of the advantages of H2 is that it is in-memory, which means that data is stored in the computer’s main memory instead of on disk. This makes it very fast for read and write operations, but also means that data is not persisted when the application is closed. However, H2 also supports disk-based storage and can be configured to persist data on disk.
H2 is often used for testing and prototyping, as well as small to medium applications that don’t require a large enterprise-grade database system. It can be integrated with popular frameworks like Spring and Hibernate, and supports a variety of data types, including JSON, XML, and spatial data.
Overall, H2 is a lightweight, fast, and easy-to-use database system that provides a useful alternative to traditional relational database management systems.
Testing
18. What are the differences between unit tests and integration tests?
Unit tests:
Unit tests are designed to test individual units of code, such as methods or functions, in isolation from the rest of the system. They are typically written by developers and focus on ensuring that individual units of code behave correctly and produce the expected result given a specific input. Unit tests are typically small in scope and run quickly.
In Java, unit tests are usually implemented using a testing framework, such as JUnit or TestNG. They often use mocking frameworks, like Mockito, to mock dependencies and isolate the code under test.
Integration testing:
Integration testing is designed to test the interactions between different components or services in a system. They are typically written by testers or QA engineers and are focused on ensuring that the system as a whole behaves correctly and produces the expected result in response to a specific set of inputs.
In Java, integration tests are typically implemented using a testing framework, such as JUnit or TestNG, and often use tools like Selenium to test web applications. Integration tests may require more setup and configuration than unit tests and may take longer to run.
| Feature | Unit tests | Integration tests |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Individual code units | Interactions between different components of the system |
| Authorship | Developer | Quality control |
| Execution time | Fast due to short range | They take time due to setup and long range |
19. What is TDD?
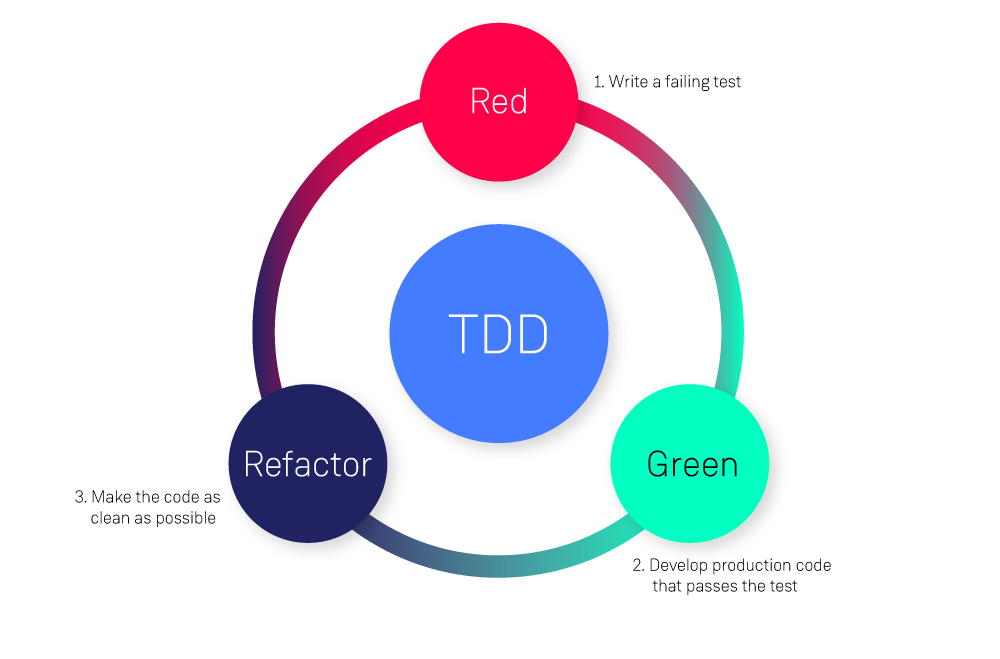
TDD (Test-Driven Development) is a software development methodology in which developers write automated tests for a feature before writing the actual code that implements that functionality. The TDD process typically involves three steps:
-
Write a failed test: The developer writes a test that describes the desired behavior of the code, but it fails because the code doesn’t exist yet.
-
Write the code – The developer then writes the minimum amount of code necessary for the test to pass.
-
Refactor the code – Once the test passes, the developer can refactor the code as needed to improve its design to maintain it, without changing its behavior.
By following this process, TDD aims to produce high-quality code that is correct and maintainable. TDD can also help ensure that code is compliant and that code changes do not introduce new bugs.
Some advantages of TDD include:
-
Improved code quality: TDD can help ensure that code is correct, reliable, and maintainable, which can reduce the cost of development and maintenance over time.
-
Faster feedback: By writing tests first, TDD provides faster feedback to the developer, which can help catch and fix bugs earlier in the development process.
-
Reduced regression bugs: TDD can help catch regression bugs by running tests automatically and ensuring that code changes don’t break existing functionality.
-
Better design: By focusing on testing first, TDD can foster better design practices such as loose coupling, high cohesion, and dependency injection.
However, TDD can also have some disadvantages, such as:
-
Increased development time: Writing tests first can add additional time to the development process, especially if the tests are complex or difficult to write.
-
Difficult to test certain types of code: Some types of code, such as user interfaces or database interactions, can be difficult to test with TDD.
-
Over-reliance on tests: TDD can lead to over-reliance on tests, which may not catch all possible bugs or may miss important cases.
20. What is JUnit?

JUnit is a popular open source Java testing framework that is widely used by developers to write unit tests for their Java applications. It provides a simple and elegant way to write automated tests, making it easy to catch and fix bugs early in the development cycle.
JUnit provides a set of annotations and assertions that can be used to define and run tests. Some of JUnit’s key features include:
-
Assertions: JUnit provides a set of assertion methods that can be used to test whether a given condition is true. These assertions help verify that the code under test behaves as expected.
-
Annotations: JUnit provides a set of annotations that can be used to define tests, configure fixtures, and control the flow of test execution.
-
Test runner: JUnit provides a test runner that can be used to perform tests and report the results.
-
Test suites: JUnit allows tests to be grouped into suites, which can be run together.
JUnit is widely used in Java development and is supported by many integrated development environments (IDEs) such as Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, and NetBeans. Its popularity and wide adoption have led to the development of many third-party tools and libraries that extend its functionality and make it even more powerful.
class ExampleServiceTest {
@Mock
private ExampleRepository exampleRepository;
@InjectMocks
private ExampleService exampleService;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
}
@Test
void testGetObjectById() {
Long id = 1L;
Example expectedObject = new Example();
when(exampleRepository.findById(id)).thenReturn(expectedObject);
Example result = exampleService.getObjectById(id);
assertEquals(expectedObject, result);
verify(exampleRepository, times(1)).findById(id);
}
@Test
void testCreateObject() {
Example object = new Example();
exampleService.createObject(object);
verify(exampleRepository, times(1)).save(object);
}
@Test
void testUpdateObject() {
Example object = new Example();
exampleService.updateObject(object);
verify(exampleRepository, times(1)).save(object);
}
@Test
void testDeleteObject() {
Long id = 1L;
exampleService.deleteObject(id);
verify(exampleRepository, times(1)).deleteById(id);
}
}
21. What is AssertJ?
AssertJ is a Java library that provides a set of fluent assertions that make it easy to write readable and expressive unit tests. It is built on top of JUnit and other test frameworks, providing a simple and elegant way to write assertions that can improve the readability and maintainability of your tests.
Some examples of AssertJ statements include:
-
assertThat(): This is the main entry point to the AssertJ library. Takes a real value and returns an instance of the Assert object, which can be used to chain assertions together.
-
isEqualTo(): This assertion checks if two objects are equal, using the equals() method.
-
isNotNull(): This assertion checks if an object is not null.
-
hasSize(): This assertion checks if a collection has a specific size.
-
contains(): This statement checks if a collection contains a specific element.
Here’s an example of how AssertJ can be used to write a unit test:
@Test
public void testSum() {
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
int result = calculator.sum(2, 3);
assertThat(result).isEqualTo(5);
}
In this example, we create an instance of the Calculator class and call its sum() method with two integer values. We then use the assertThat() method to assert that the result is equal to 5. The isEqualTo() method is used to check if the actual value is equal to the expected value.
Using AssertJ can help make your tests more readable and expressive, making it easier to understand the intent of the test and the expected behavior of the code being tested.
Design Patterns and Principles
22. Explain the purpose and application of the most used design patterns: Builder, Factory Method, Abstract Factory, Adapter, Singleton
Design patterns are reusable solutions to common software design problems that have proven their worth over time. Here are explanations of some of the most commonly used design patterns:
-
Builder: This pattern is used to create complex objects by breaking the object building process into smaller, simpler steps. It provides a flexible and easy-to-use solution for creating complex objects without having to deal with complex constructors or multiple constructors.
-
Factory Method: This pattern is used to create objects without specifying the exact class of object to be created. Instead, the factory method creates objects by calling a method on a factory object that creates the appropriate object based on the supplied inputs.
-
Abstract Factory: This pattern is used to create families of related objects without specifying the exact classes of objects to be created. It provides an interface for creating families of related objects, which can be implemented by various concrete factory classes.
-
Adapter: This pattern is used to convert the interface of a class to another interface that clients expect. It is useful when the interface of an existing class does not match the interface that a client expects.
-
Singleton: This pattern is used to ensure that only one instance of a class is created and that it can be accessed globally throughout an application. It provides a way to centralize access to a single instance of an object, and is often used in cases where you need to control access to resources or ensure data consistency.
In general, these design patterns provide useful solutions to common software design problems and can help improve the efficiency, flexibility, and maintainability of software applications.
23. Explain the following principles of software development: DRY, KISS, SOLID
DRY (Don’t Repeat Yourself)
This principle states that each piece of knowledge or logic in a system must have only one representation. In other words, it advocates reducing code duplication and promoting code reuse. By adhering to this principle, developers can reduce the amount of code they need to write, which can save time and reduce the risk of introducing bugs into the code base.
KISS (Keep It Simple, Stupid)
This principle advocates simplicity in software design. It suggests that software should be kept simple and easy to understand, rather than being overly complex. Simple software is often easier to maintain, test, and debug, and can also be more efficient than complex software.
SOLID
SOLID is an acronym that stands for five software design principles that are used to promote good software design practices.
-
Single Responsibility Principle (SRP): This principle states that each class should have only one responsibility and should only be responsible for one thing. This makes the code easier to maintain, test, and modify, since changes made to one responsibility will not affect other responsibilities.
-
Open-Closed Principle (OCP): This principle states that software entities should be open for extension but closed for modification. In other words, developers should be able to add new features to the system without modifying existing code. This helps promote code reuse and reduces the risk of introducing bugs into existing code.
-
Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP): This principle states that objects of a superclass must be replaceable with objects of a subclass without affecting the correctness of the program. This helps ensure that the code is more maintainable and can be easily extended.
-
Interface Segregation Principle (ISP): This principle states that clients should not be forced to depend on interfaces that they do not use. This helps keep the code clean and simple, and makes it easier to understand and maintain.
-
Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP): This principle establishes that high-level modules should not depend on low-level modules, but both should depend on abstractions. This helps reduce coupling between different parts of the system, making the code more flexible and maintainable.
Miscellaneous Knowledge
24. After discovering an error or defect in a part of the production code, what criteria can you use to classify it?

When a bug or defect is discovered in production code, it can be classified using various criteria. Some common criteria that can be used to classify errors are:
-
Severity: Refers to the severity of the bug in terms of its impact on the application or system. Bugs can be classified as critical, major, minor, or trivial based on their severity.
-
Priority: Refers to the importance of fixing the bug relative to other bugs and tasks that need to be addressed. Bugs can be classified as high, medium, or low priority based on their urgency and impact.
-
Reproducibility: refers to the consistency with which the error can be reproduced. Errors can be classified as reproducible or non-reproducible.
-
Root Cause: This refers to the underlying reason for the error. Bugs can be categorized based on their root cause, such as coding bug, design flaw, or environmental issue.
-
Area of impact: refers to the specific part of the application or system that is affected by the error. Bugs can be categorized based on their area of impact, such as the user interface, database, or network.
-
Frequency of Occurrence: This refers to the frequency with which the error occurs. Errors can be classified as intermittent, sporadic, or constant based on their frequency of occurrence.
-
Test Coverage: Refers to how well the bug was covered in the testing process. Bugs can be classified based on their test coverage, such as missing in unit tests, integration tests, or regression tests.
By using these criteria, developers and testers can prioritize and manage the bug fix process and improve the overall quality of the software product.
25. Explain RESTful and HTTP semantics
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style for creating web services. It is based on a set of restrictions that emphasize the use of HTTP protocols to access and manipulate resources. RESTful web services provide a uniform interface that allows different clients to communicate with a server over the Internet.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is a protocol used to transfer data between a client and a server over the Internet. It is based on a request-response model, where clients send requests to servers, and servers respond with a message containing the requested information. HTTP defines a set of methods (also called verbs) that can be used to interact with resources on a server.
RESTful web services use HTTP methods to interact with resources. The most common HTTP methods used in RESTful web services are:
- GET: It is used to retrieve a representation of a resource.
- POST: It is used to create a new resource.
- PUT: It is used to update an existing resource.
- DELETE: It is used to delete a resource.
In addition to HTTP methods, RESTful web services also use URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers) to identify resources. URIs are used to locate resources on the server and follow a hierarchical structure. For example, a URI for a resource might be https://example.com/customers/123.
HTTP semantics refers to the meaning and use of HTTP methods, headers, and status codes. HTTP methods are used to indicate the desired action to be performed on a resource, while HTTP headers provide additional information about the request or response. HTTP status codes are used to indicate the result of a request.
Some common HTTP status codes include:
- 200 OK: The request was successful.
- 201 Created: The resource was created successfully.
- 400 Bad Request: The request is invalid or has an incorrect format.
- 401 Unauthorized: The request requires authentication or authorization.
- 404 Not Found: The requested resource was not found.
- 500 Internal Server Error: An error has occurred on the server.
Understanding RESTful and HTTP semantics is essential for creating and consuming web services. It allows developers to write code that follows best practices and is interoperable with other systems.

